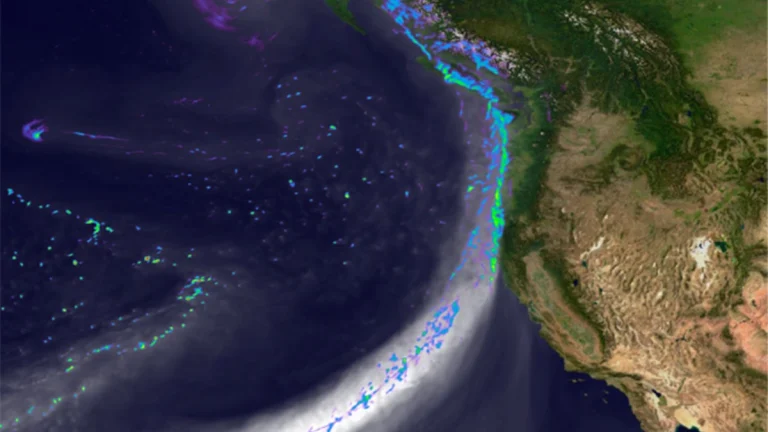
U.S. West flood risk increases sharply with wet soils during atmospheric river storms
Wet antecedent soil moisture increased streamflow magnitudes by 2–4.5 times during atmospheric river storms across 122 U.S. West Coast watersheds between 1980 and 2023, according to a new analysis. The study, published in the Journal of Hydrometeorology on June 4, 2025, establishes a nonlinear threshold effect in soil moisture, above which flood response to atmospheric rivers increases sharply.